Citizen as Sensor/Crowd Sensor is the first step in the process to use the citizen generated data as an input to make the city smarter.
The first step in the process to make a city smart is using the intelligent feedback from citizens found on the social networks.
In today’s world, citizens owning a mobile device can be transferred into active and passive sensors. For cities who are smart, it means they don’t always need to invest in expensive physical sensor infrastructures with a very high cost of maintenance.
Social network users (read citizens) are not only creators and recipients of the information, but citizens are also adding value in interpreting critical relays to propagate information and from their common sense of identifying suspicious situations. No doubt that the wealth of information in the social networks and involvement of citizens is heavily underused in cities and that’s why Fidecity invested in big data and sentiment analysis tools to gather that information.
The citizen communication via social media (e.g.Facebook, Twitter, Instagram etc.) can provide cities with valuable information. Fidecity is making the big data actionable !
Some applications of social listening:
Crisis Detection and Management
Probably the biggest relevant research area which social media has stimulated has been in the domain of crisis detection and management (Kavanaugh et al., 2012). By providing live access into the thoughts, feelings and opinions of citizens, social media are uniquely positioned to be able to highlight unusual events or crises as they emerge, or perhaps even before then. Importantly, this can take place much faster than conventional crisis highlighting mechanisms.
Citizens love to report almost real-time disaster related data such as flooding, fire, accident etc. via Twitter and other social media platforms which allows Fidecity to alert emergency and security personal in the city.
We can compare two or more cities and check how they are performing with their communication on the social networks. The share of voice info is gathered during the same timeframe in a city.
Social and Demographic Data Collection
Social media data is a substitute for traditional data capture techniques, such as surveys, which are costly and time consuming. Social media data offer cheaper and faster results. Especially with the rise of mobile applications, there is a huge opportunity to explore the use of social media data for traffic and mobility analysis.
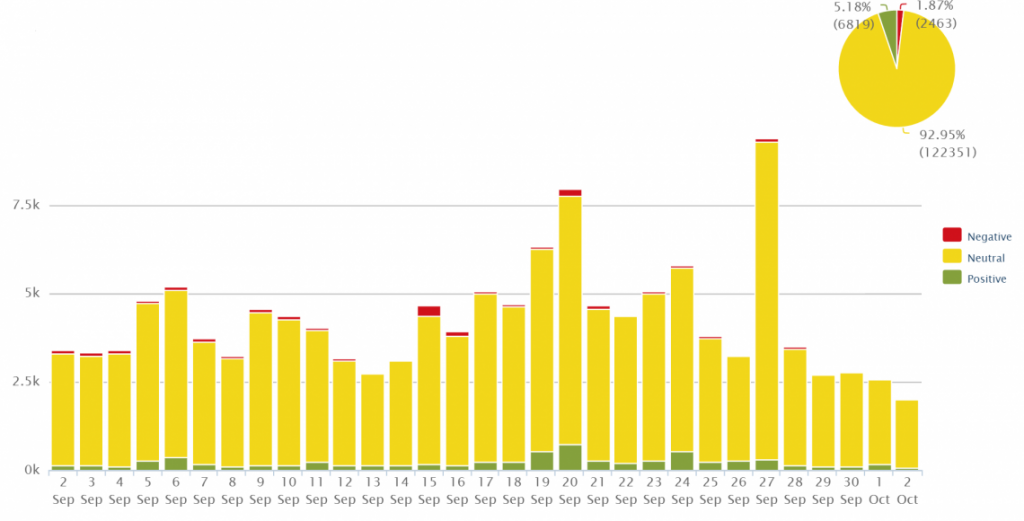
Sentiment
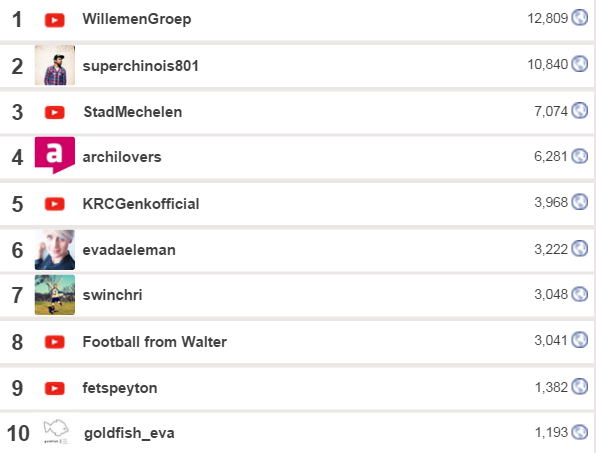
Top ten authors
Which communicator makes impact ?
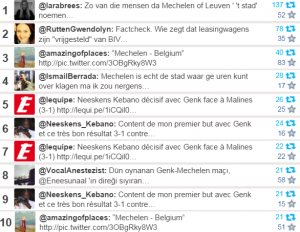
Top ten mentions

What are ‘the stories’ in your city !
Top ten retweets
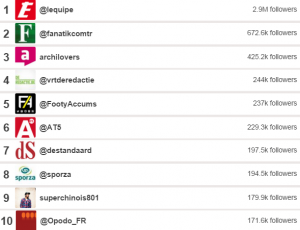
Top ten influencers
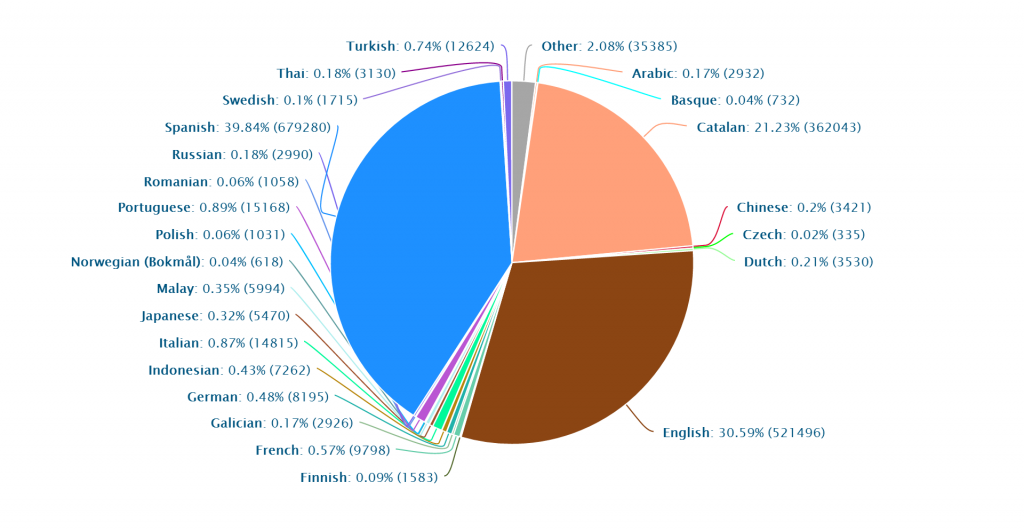
Languages Barcelona
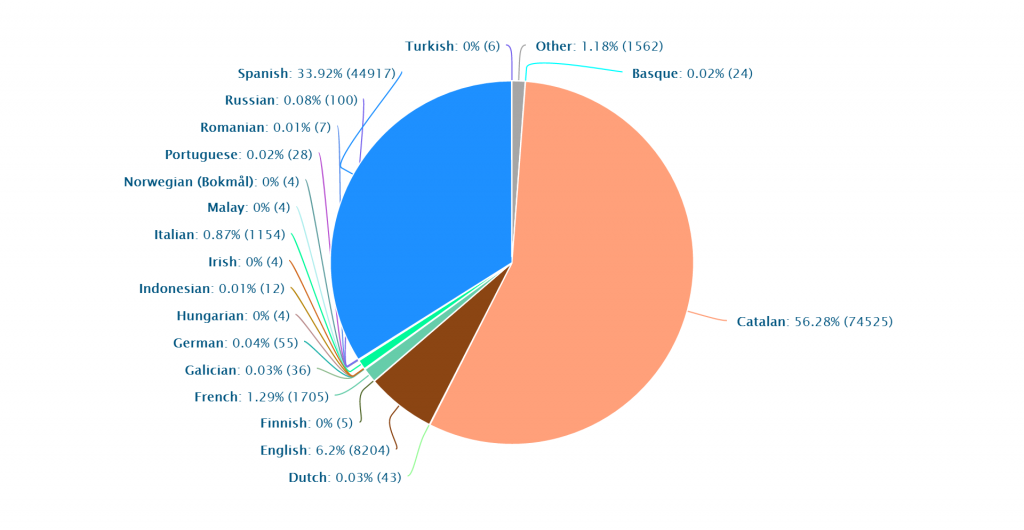
Languages Tarragona
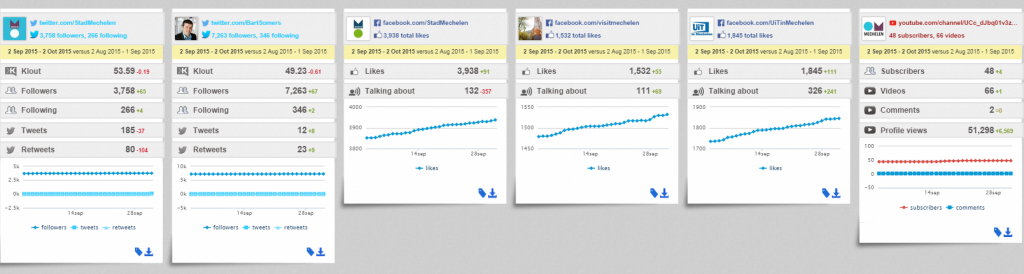
City Communication Channels – Share of Voice
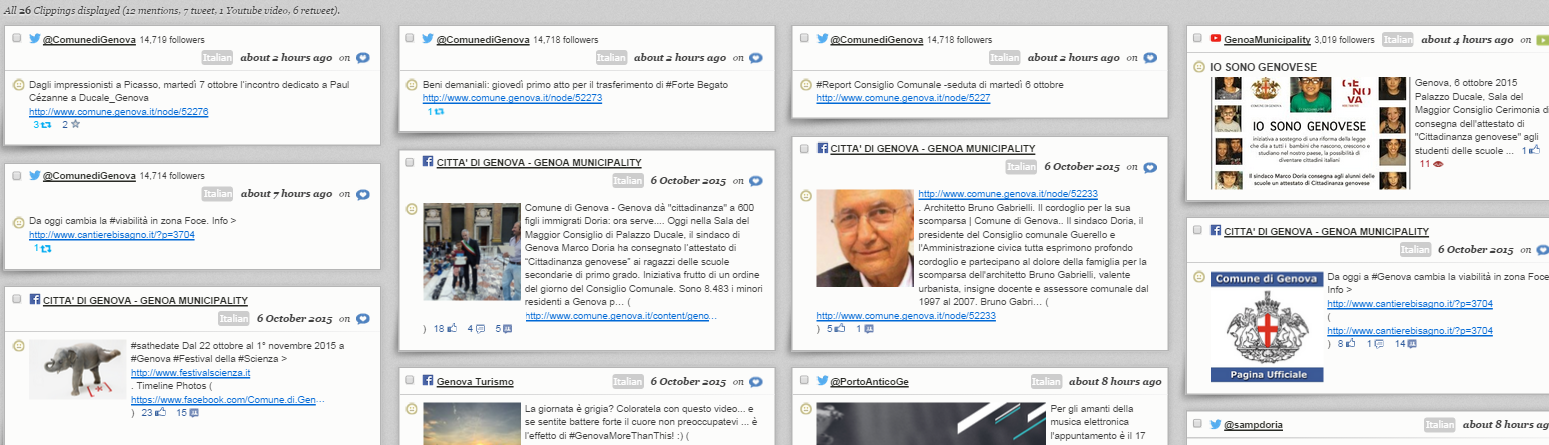
Clippings -what is being said about the city
What are the key topics citizens talk about ?

Share of voice
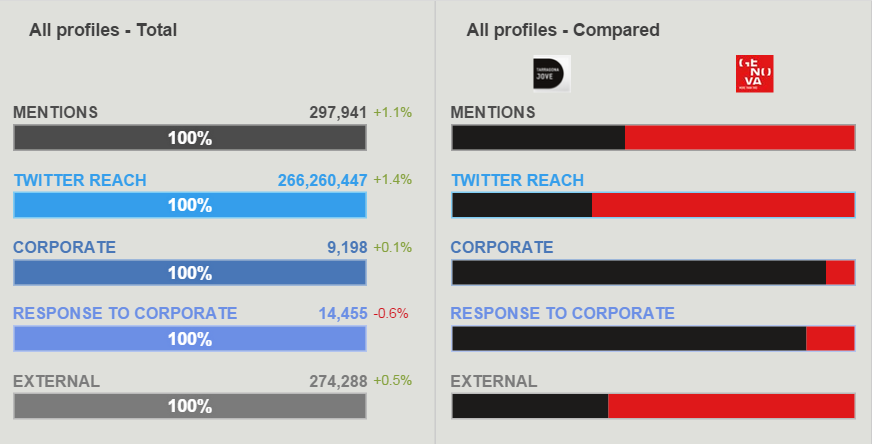
Share of voice
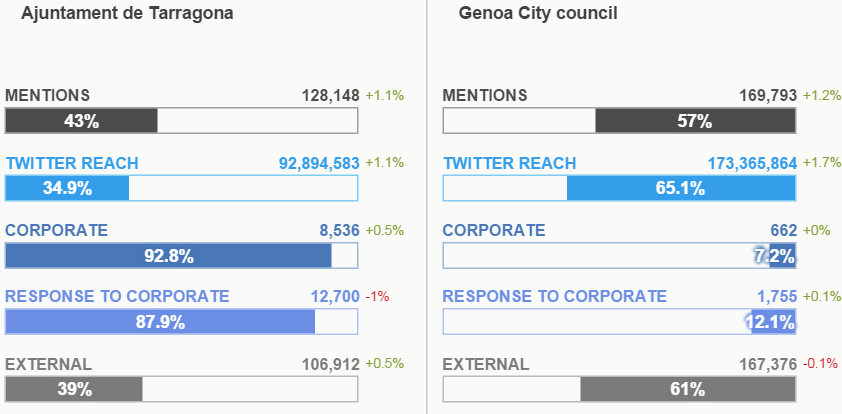
Let’s analyze this chart ! Both cities have a good amount of mentions.
Genoa’s reach (173365884) is a lot higher then Tarragona’s (92894583) reach. Genoa is reaching more then 173 million people on Twitter.
However, Tarragona does take a huge chunk of the responses to corporate category, showing that their citizens and interested parties are far more engaged with Tarragona than the Genoa ones. In fact, it’s a good example that even if you have the ability to reach 80 million more people, Tarragona is a lot more efficient and has a lot more engaged people.
Spacial and Regional Planning
Intermunicipal cooperation (or lead and follower cities) will be a major challenge for spatial and regional planning to create transmunicipal central places in the future. Fidecity can analyze which cities are already “connected” to each other today.


